Transaction
Transaction
A unit of program execution that accesses and possibly updates various data items
2 main issues to deal with
- Failure of various kinds (e.g. hardware failure, system crash)
- Concurrent execution of multiple transaction
ACID
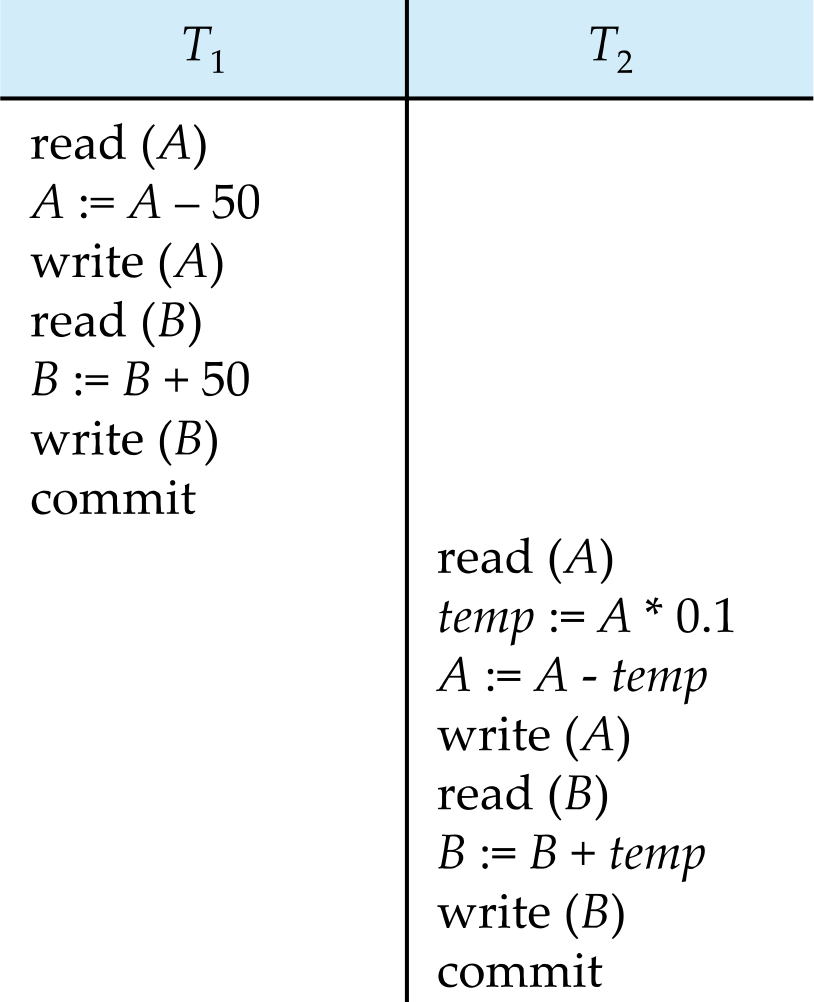
Atomicity Requirement
- Step 3 - step 6 사이에서 fail이 난다면, A의 balance가 -50이 될거야 !!Inconsistency!!
- 이런 inconsistency in database should not happen
- 부분 적으로 실행된 transaction은 db에 반영되면 안된다.
- ALL OR NOTHING
Consistency Requirement
- Explicit Integrity Constraints: Primary key, foreign key들이 유지 되어야 한다.
- Implicit(암묵적인) integrity constraints: e.g. sum of balances of all accounts, minus sum of loan amounts must equal value of cash-in-hand
- 우리 예시에서 보자면 transaction 전, 후의 balance total은 같아야해
Isolation Requirement
- 여러 개의 Transation이 동시 실행 될때 transation들이 서로에게 영향을 주면 안된다.
Durability Requirement
- Transaction이 성공적이 였다면, 수행한 결과는 DB에 반영 되어야 하고 storage에 저장되어 must persis even if there are software or hardware failures.
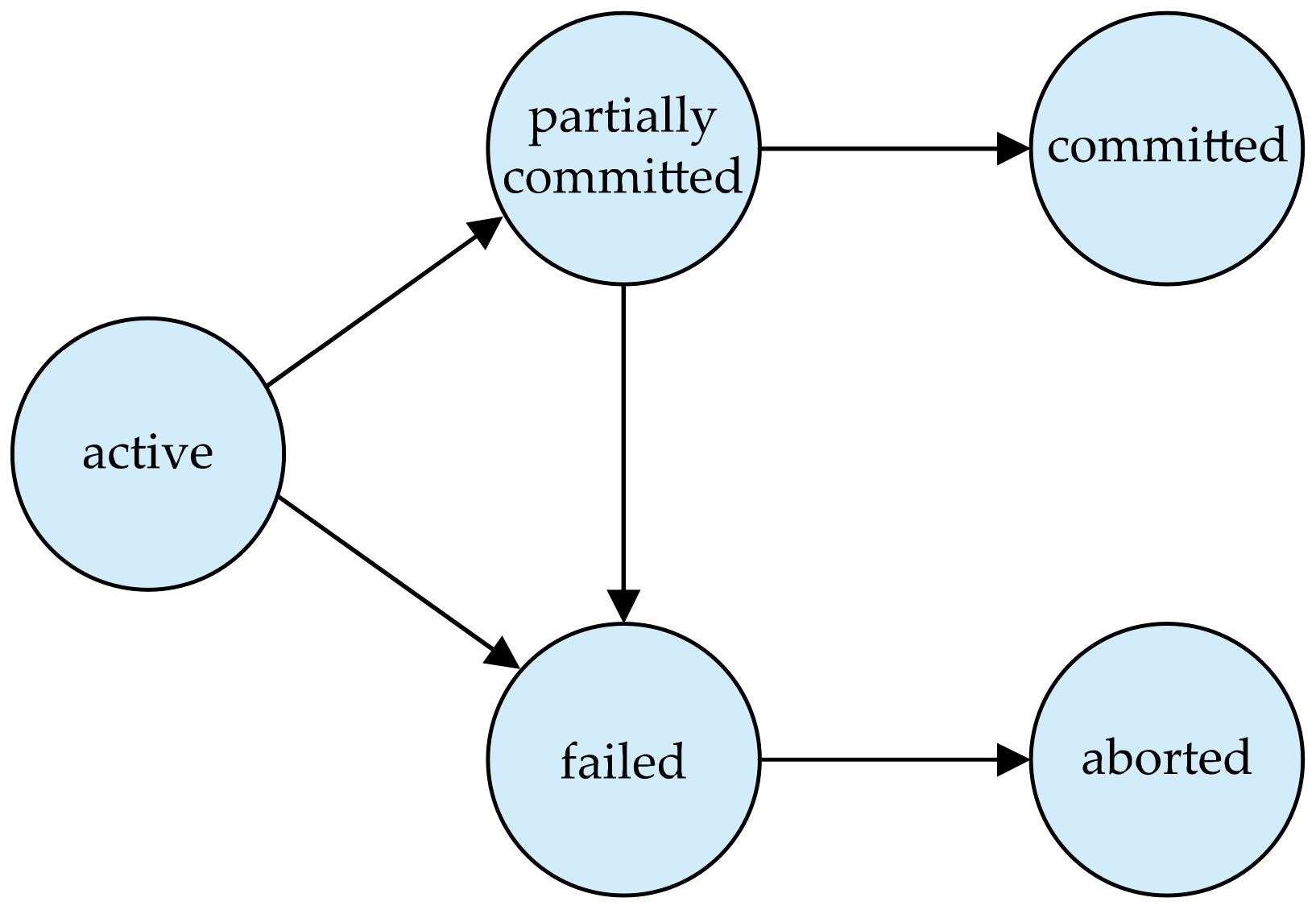
Transaction State
Common Sense로 넘어 갈수 있는건 넘어가겠다.
- Partially committed: transaction이 실행할 모든 명령문을 성공적으로 마쳤지만, 아직 완전히 커밋되어 최종 결과가 디스크에 반영되기 전의 상태
- Aborted: State after the transaction has been rolled back and the database restored to its state prior to the start of the tranation.
- Two options after it has been aborted
- Restart the transaction
- Kill the transaction
- Two options after it has been aborted
- Committed: State after successful completion
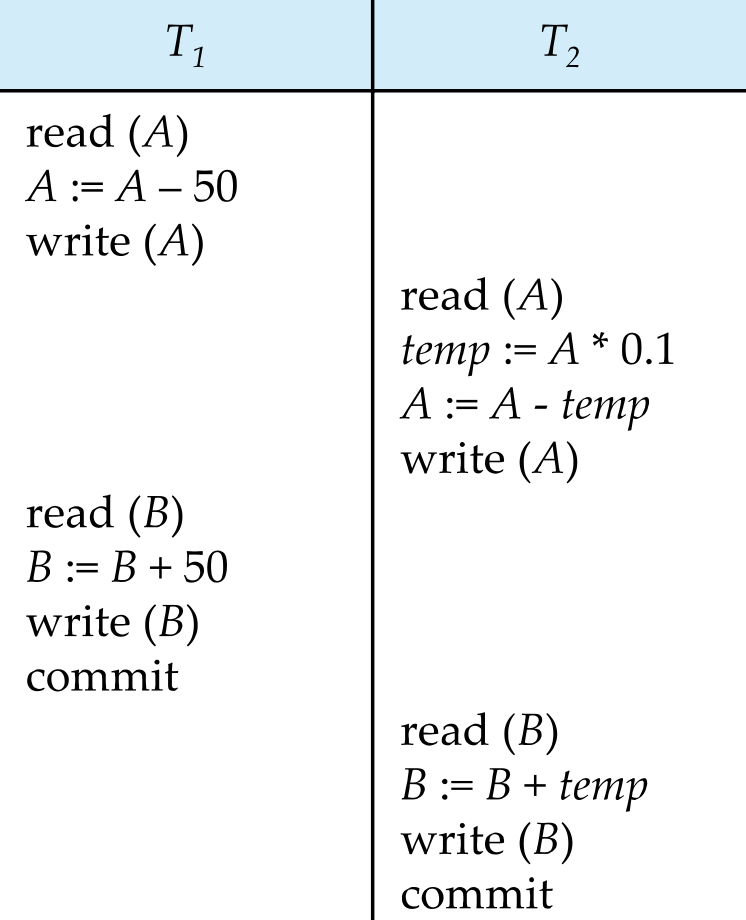
Schedules
Specify the order in which instructions of concurrent transations are executed </br> Transaction들 끼리의 내부 연산들이 어떻게(in which order) 실행되는지에 대한 것
- transation이 성공적으로 끝나면 commit이 될거야
- fail하면 abort instruction이 진행되겠지
Serializability
Serializable
A schedule is serializable if it is equivalent to a serial schedule: 결과가 동일하면 돼
Serial schedule
- T1 -> T2 순서대로 실행된다.
- T1, T2 내부의 연산들의 순서가 바뀌었지만 앞의 serial하게 실행된거랑 같다.
- => Serializable Schedule
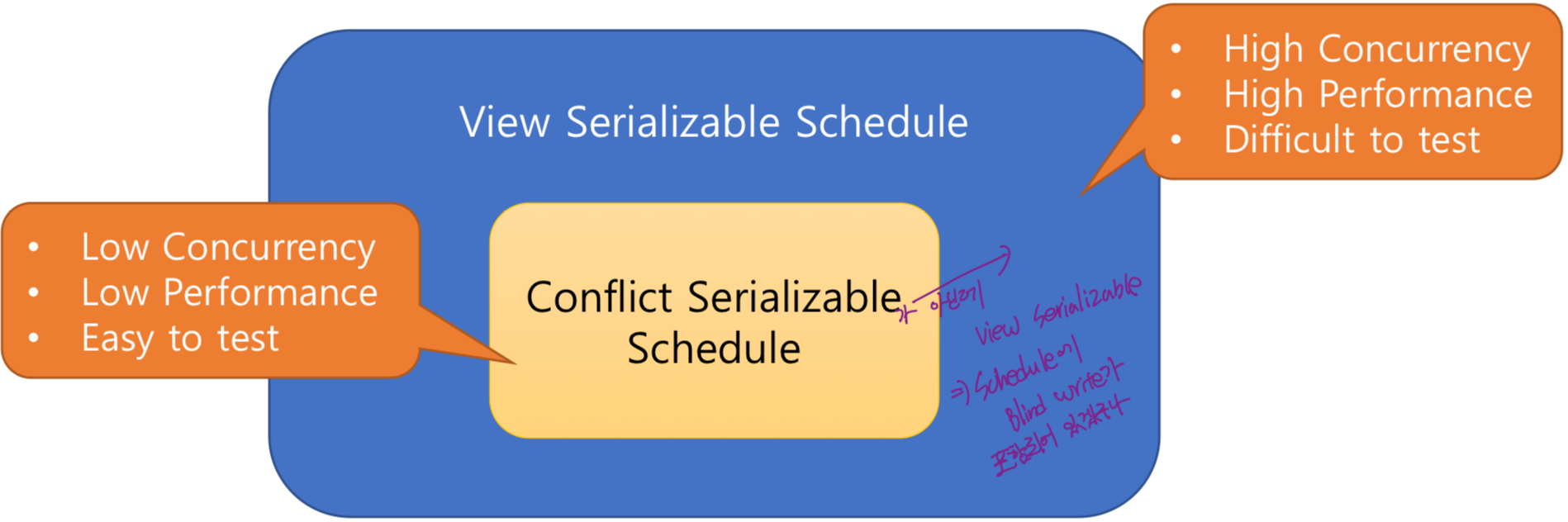
Conflict Serializability
If a schedule S can be transformed into a schedule S’ by a series of swaps of non-conflicting instructions, we say that S and S’ are conflict equivalent.
- Conflict Serializable: conflict equivalent to a serial schedule
- 위 Serial schedule에 나온 예시도 보면 conflict serializability야
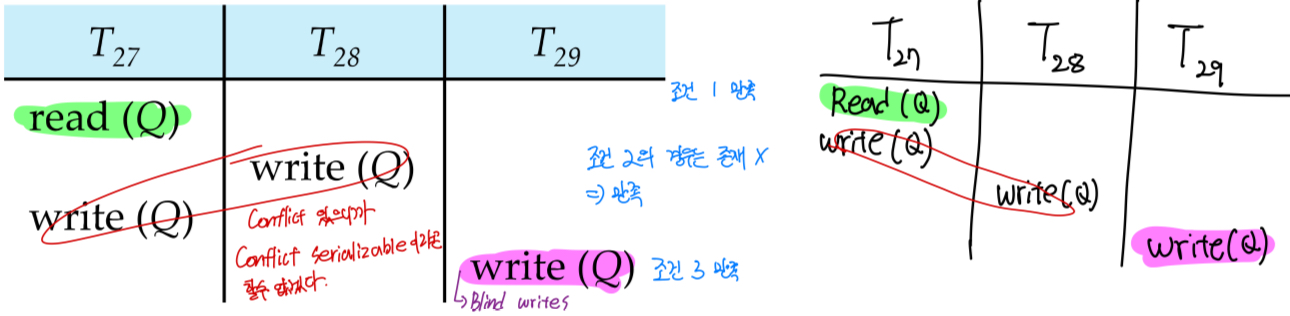
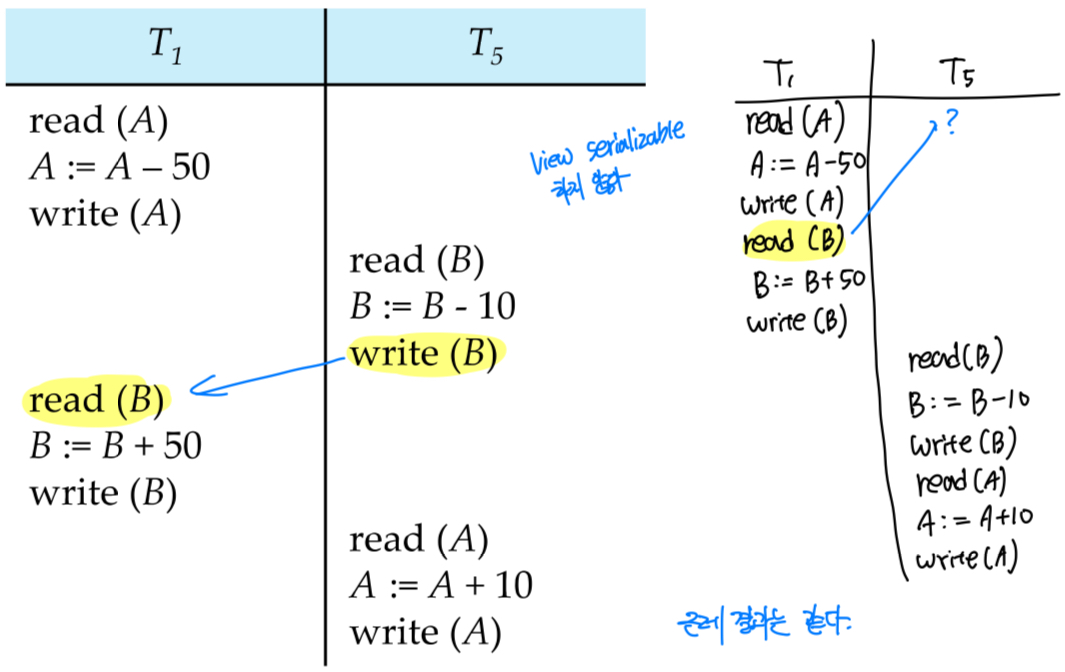
conflict serializable하지 않은 예시
Conflict
- Conflict forces an order between them
View Serializability
조건
- S에서 Ti가 Q의 초기값을 읽으면 S’도 Ti가 Q의 초기값을 읽어야 한다.
- S에서 Tj에 의해 생성된 값 Q를 Ti에서 읽으면 S’에서도 Ti가 같은 Tj의 연산에 의해 만들어 Q값을 읽어야 한다.
- S의 Q에 대한 마지막 연산 write(Q)가 실행 되였다면, S’에서도 Q에 대한 마지막 연산은 S와 같은 write(Q)이여야 한다.
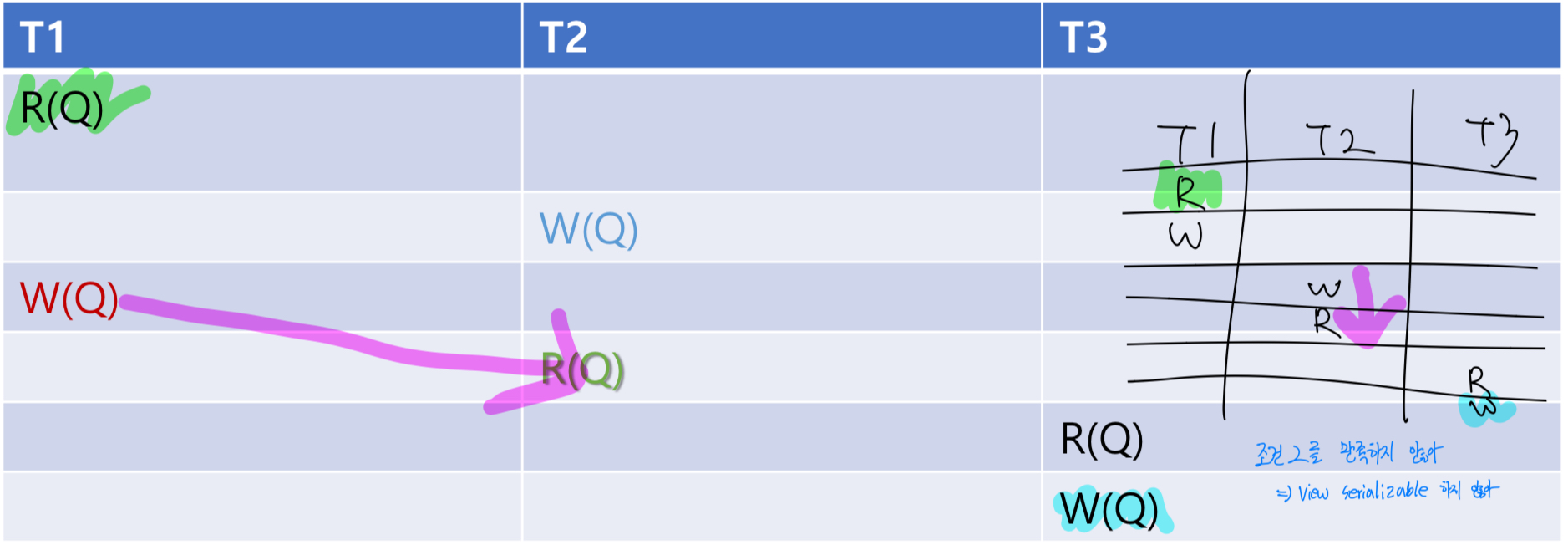
 view serializable, conflict serializable 아니지만, 결과는 똑같아, 사칙연산과 같은 경우 결과가 같음을 따지려면 내부를 고려 해봐야 해
view serializable, conflict serializable 아니지만, 결과는 똑같아, 사칙연산과 같은 경우 결과가 같음을 따지려면 내부를 고려 해봐야 해
Blind Writes
전에 쓰기 연산을 했지만, 마지막 최종 연산에 의해 덮여쓰여지기 (보이지 않기) 때문에 무시되는 write
- View serializable인데 conflict serializable 하지 않은 schedule이라면 반드시 blind write를 가지고 있다.
Testing For Serializablity
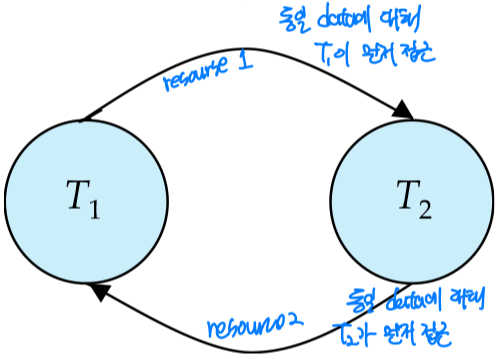 Serializability를 test하기 위해서 precedence를 사용할수 있다.
Serializability를 test하기 위해서 precedence를 사용할수 있다.
- Ti로 부터 Tj 화살표를 그엇다면
- => Ti가 먼저 동일 resource에 대해 먼저 접근하였다.
Test Conflict Serializability
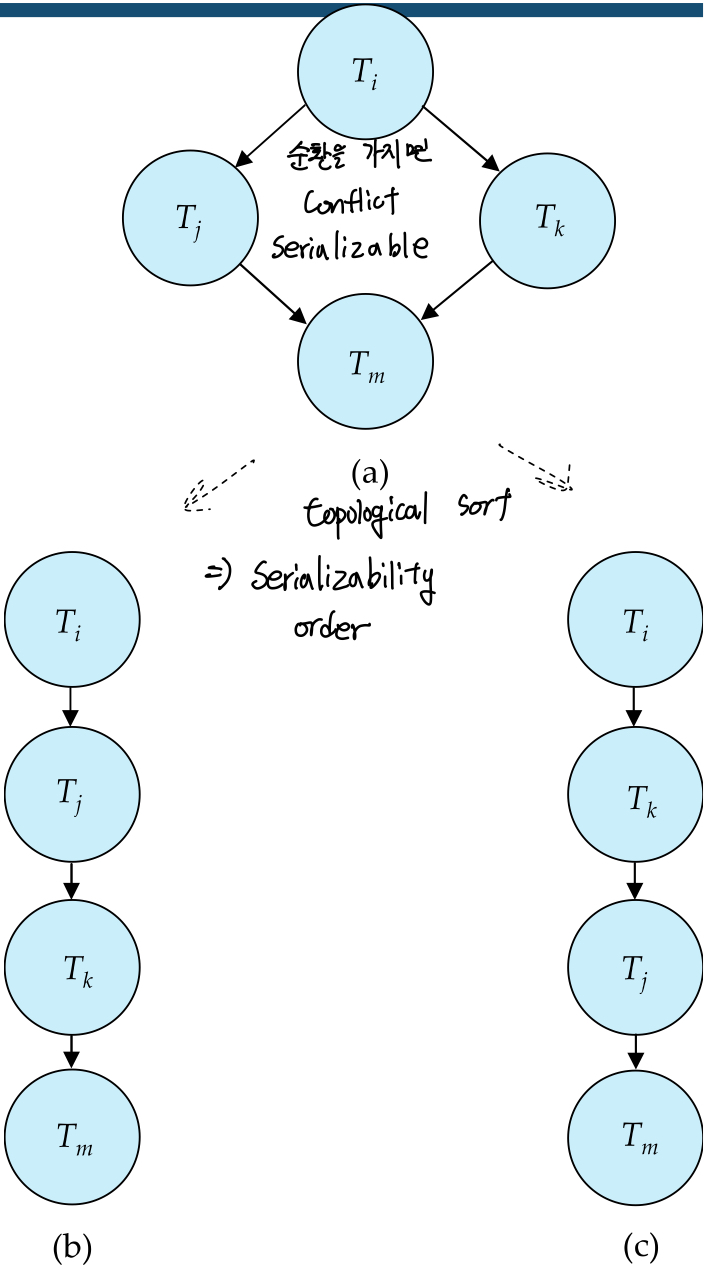 순환을 가지지 않는 다면, 이는 conflict serializable하다.
순환을 가지지 않는 다면, 이는 conflict serializable하다.
- topological sort해서 나올수 있는 결과는 serializability order이다.
Test View Serializability
NP-Complete 입니다. 너가 직접 따져보세용 ㅠ__ㅠ </br>
Recoverable & Cascading rollback
Recoveralbe Schedule
읽기-쓰기 의존 관계(read-from dependency)가 있는 두 트랜잭션 Ti -> Tj에 대해, 먼저 쓰기 주체 Ti가 커밋된 뒤에만 읽기 주체 Tj가 커밋될 수 있도록 보장하는 스케줄
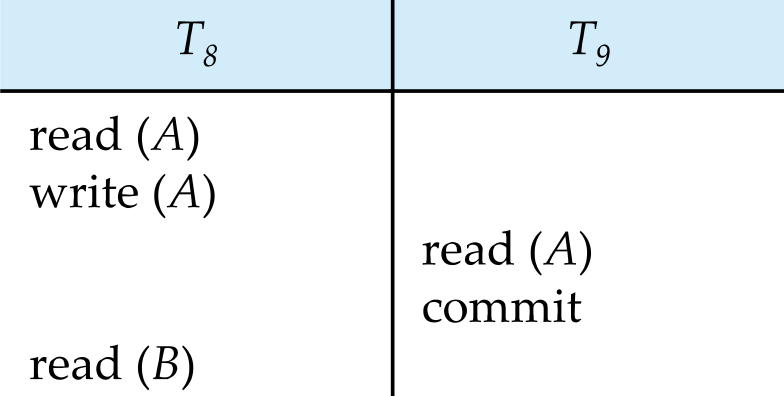 T9 commit 이후에 crash or abort가 발생해도 T9에서 commit을 해버랴서 rollback을 할수 없어
T9 commit 이후에 crash or abort가 발생해도 T9에서 commit을 해버랴서 rollback을 할수 없어
Cascading Rollback
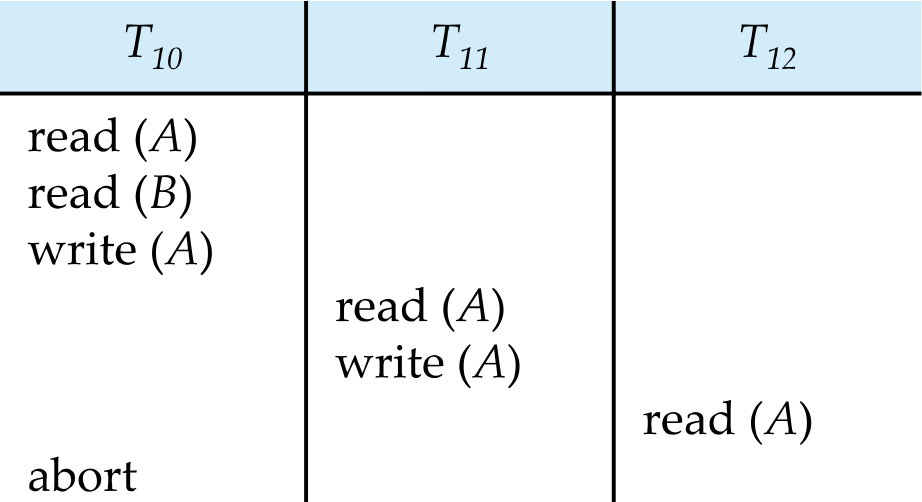 T10가 rollback된다면 T11, T12에서도 T10에서 write(A) data를 사용하기 때문에
T10가 rollback된다면 T11, T12에서도 T10에서 write(A) data를 사용하기 때문에
T10, T11, T12 모두 rollback 되어야 한다.
- 이렇게 많은 overhead가 발생하는 cascading schedule쓰지 마라탕
Cascadeless Schedule
- Read commited data only!
- Every Cascadeless schedule is also recoverable