Concurrency 1
Transaction을 먼저 보고 오세요 ㅎㅎ ^___^;;;
Concurrency Control
좋은 DBMS의 조건
- Conflict serailizable 그리고 view serailizable
- Recoverable
- Cascadeless
Trade off between the amount of concurrency they allow and the amount of overhead that they incur
Phenomena Caused By Concurrent Transaction
Dirty Read
Transaction read data written by a concurrent uncommitted transaction. (Not recoverable이게 됨)
Nonrepeatable Read
Transaction을 두번 실행하는데, data has been modified by another transaction.
Phantom Read
Transaction을 두번 실행하는데, result set has new records due to another recently-committed transaction. 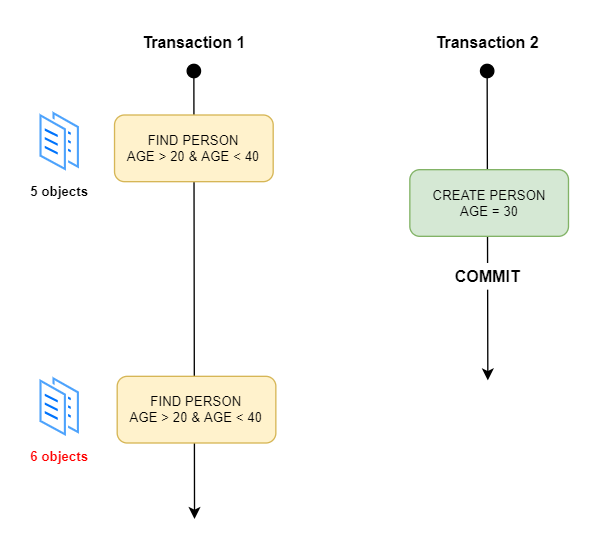
Serialization Anomaly
Result of successfully committing a group of transaction 했는데, 말이 안되는 값이 나와 (Inconsistent 해)
Transaction Isolation
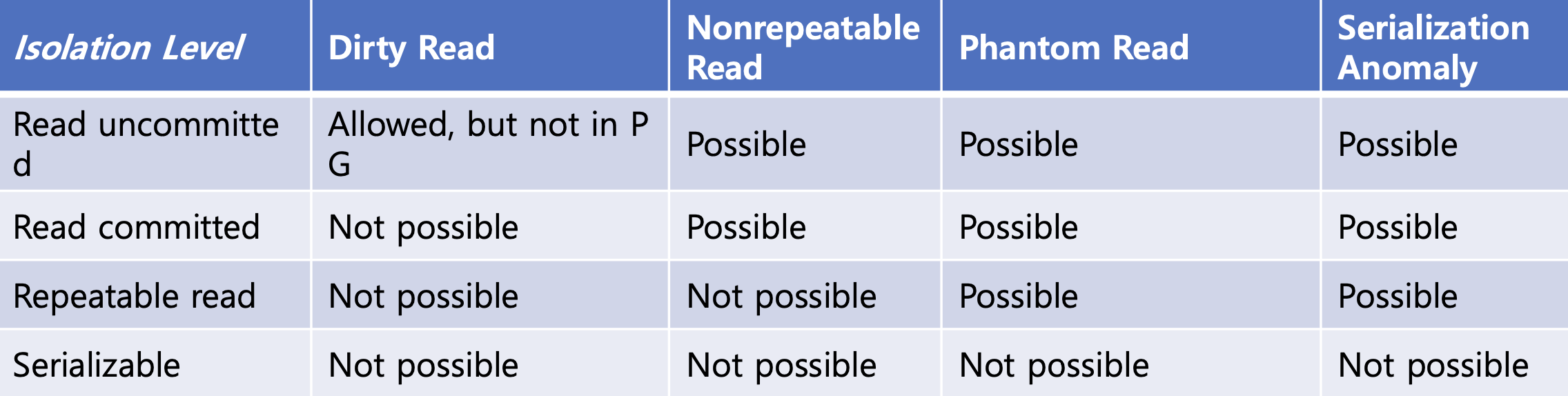 SQL-92의 Transaction Isolation Level
SQL-92의 Transaction Isolation Level
Implementation Of Isolation Levels
Locking
데이터를 못 쓰게 잠궈 버려
- Lock on whole database(concurrency no good, isolation good) VS lock on items(concurrency good, isolation no good)
- How long to hold lock
- Shared VS exclusive locks
Lock Based Protocol
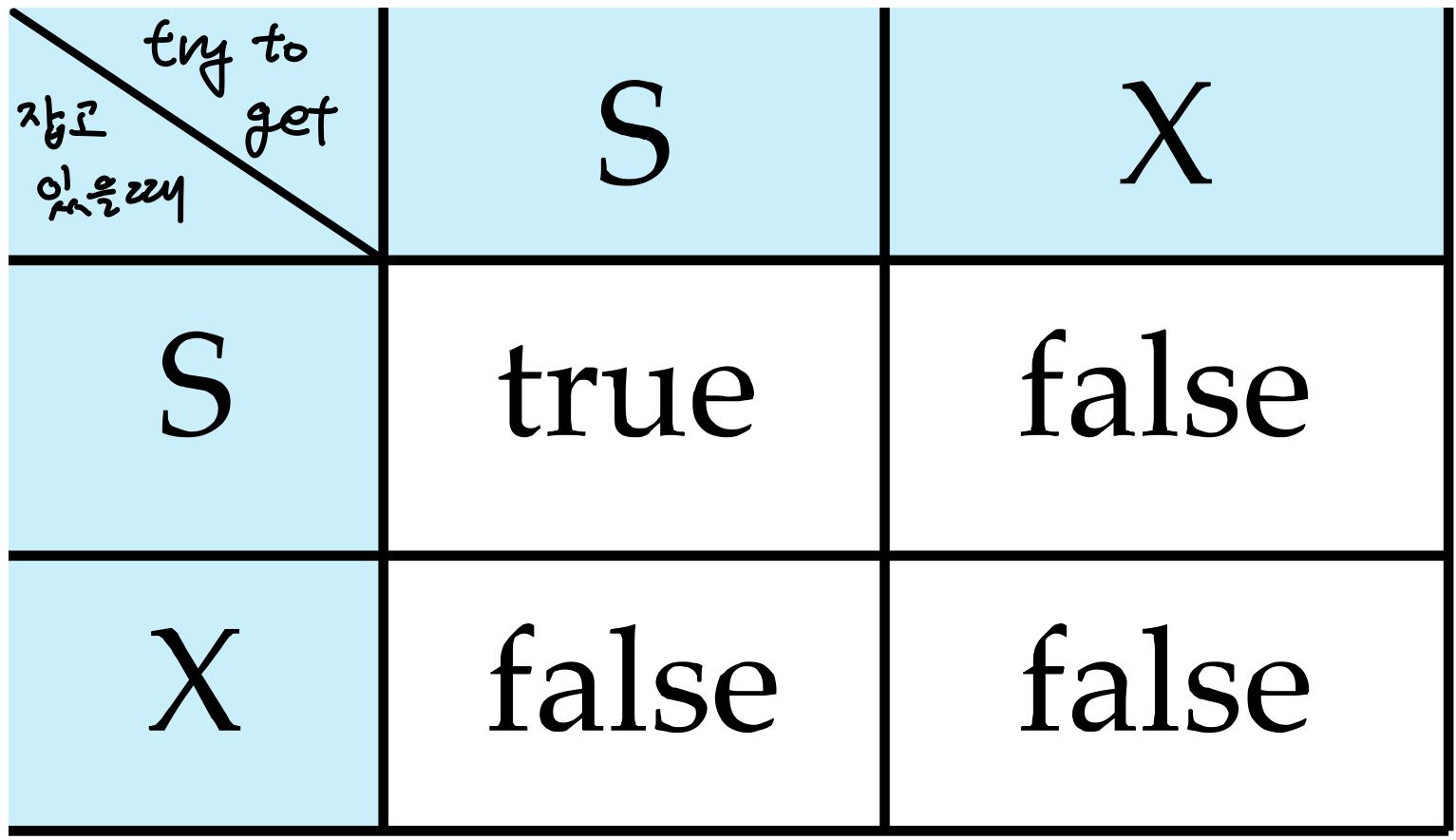
- Exclusive(X) mode: Data 읽기, 쓰기 모두 지원, 한번에 하나의 transaction만 lock을 잡을 수 있다.
- Shared(S) mode: Data 읽기만 지원, 여러 transaction이 동시 접근 가
- X-lock은 아무도 특정 resource에 대해 lock을 hold하지 않았을 때만 가능
- 특정 resource에 X-lock이 걸려 있으면 다른 X-lock, S-lock이 lock을 걸수 없어
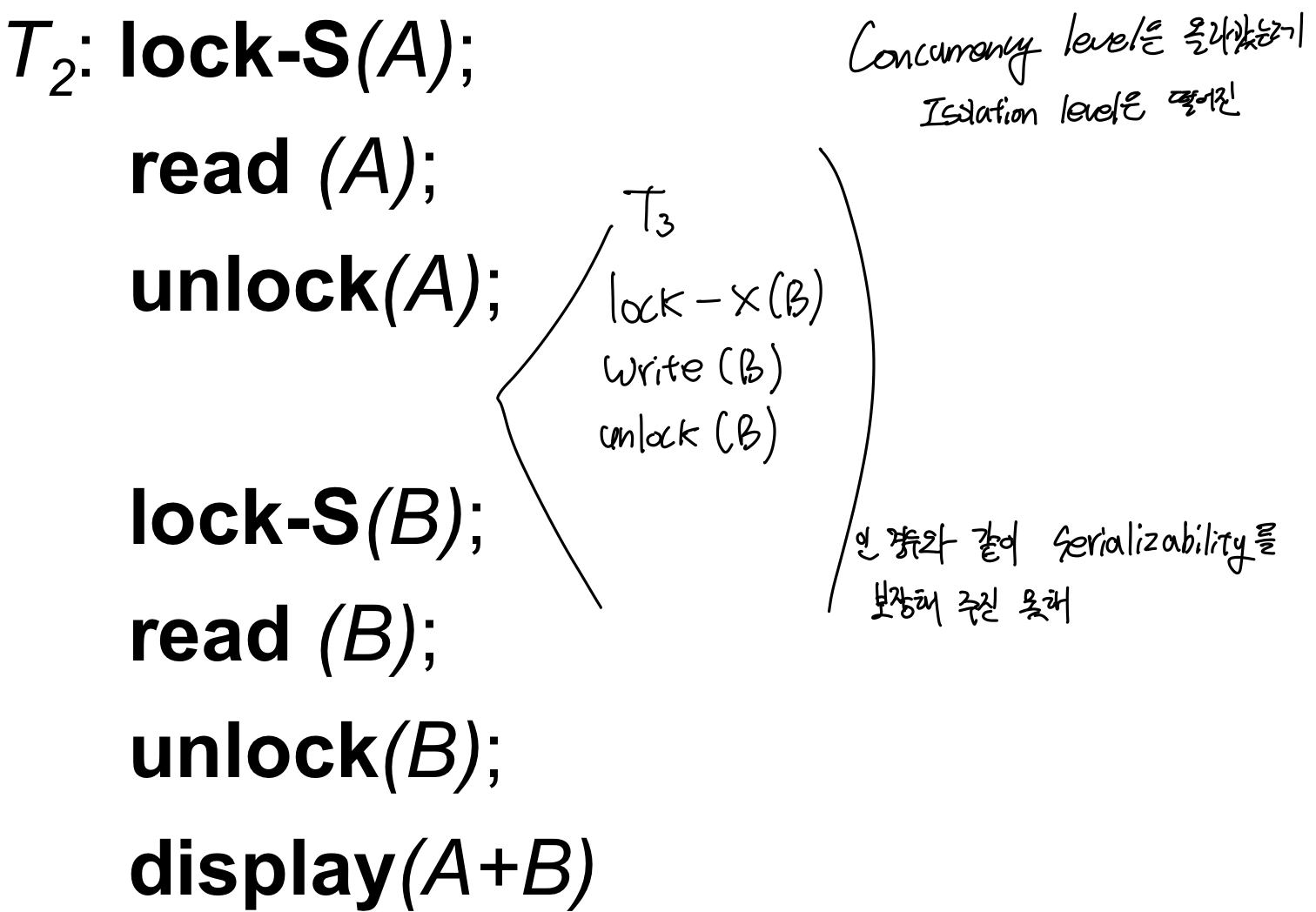
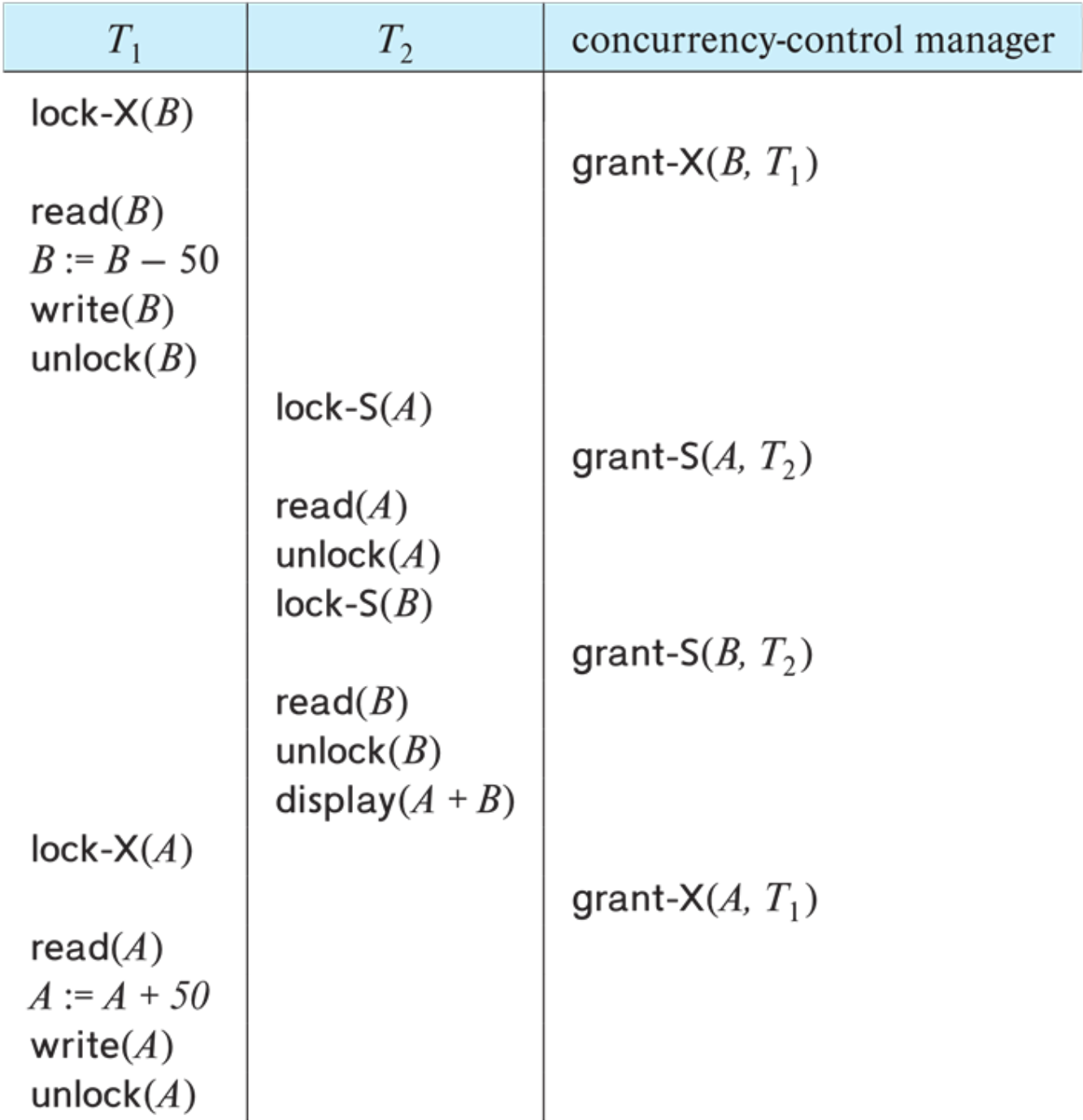 얘도 역시 serializable 하지 않는다. 동일 A에 대해 write연산이 하나 이상 있기 때문에
얘도 역시 serializable 하지 않는다. 동일 A에 대해 write연산이 하나 이상 있기 때문에
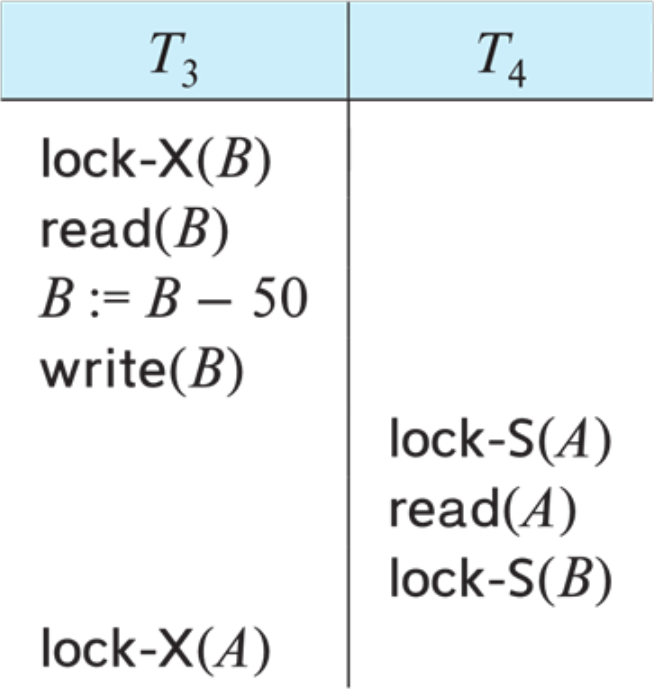
Deadlock & Starvation
T4는 T3가 끝나기를 기다리고 있고 T3는 T4가 끝나기를 기다리고 있어
서로가 서로를 기다리고 있어 무한 block되는 deadlock
Deadlock: Same transaction is repeatedly rolled back due to deadlocks
Lock Manager가 Lock을 관리하는 법
In memory data structure Lock Table로 관리한다. 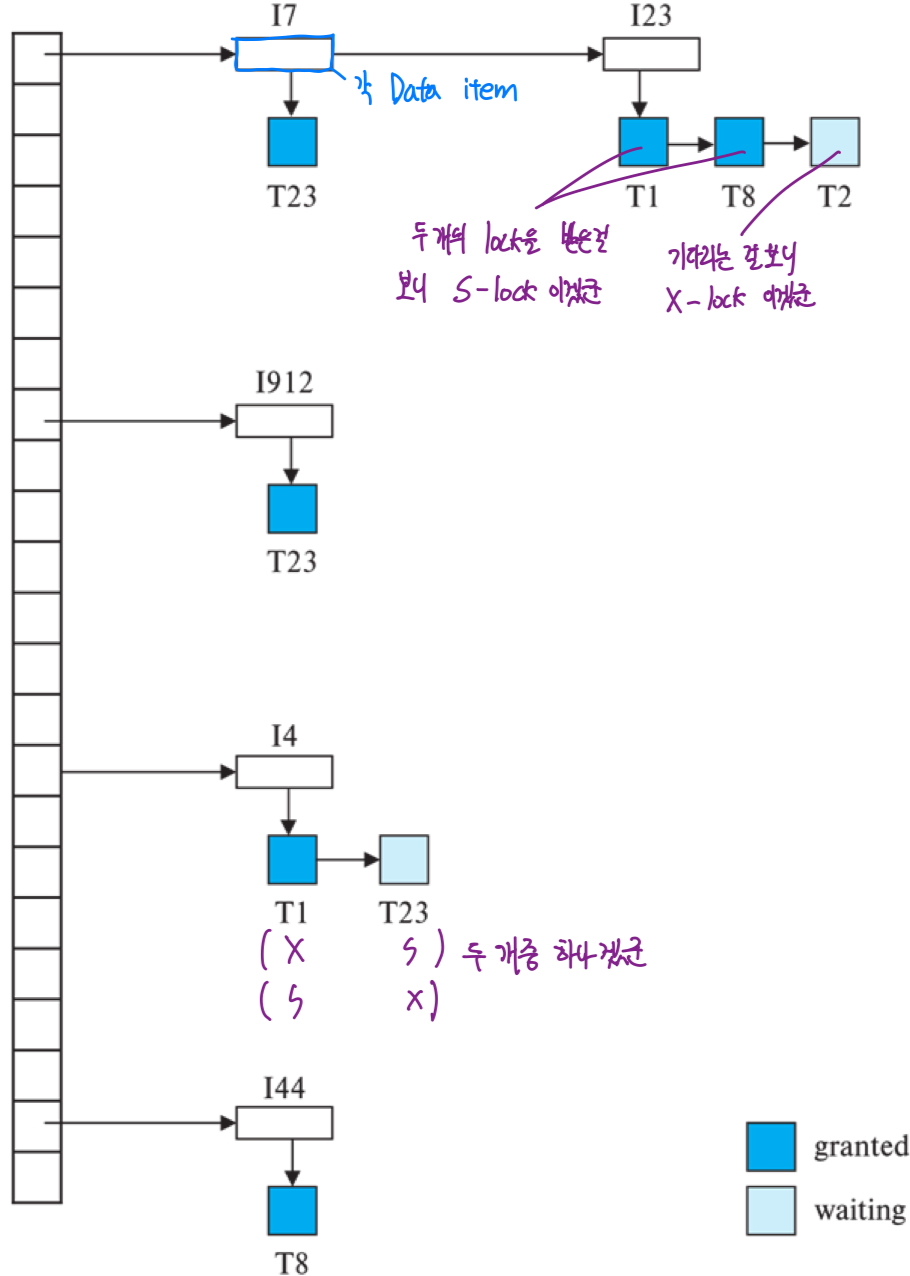
Timestamps
시간 정보를 자기도 연산들의 실행 순서를 매길게
- When Transaction timestamp assigned (e.g. when a transaction begins)
- Data items store two timestamps
- Read timestamp
- Write timestamp
- Used to detect out of order accesses
Multiple Version of each data item
Allow transactions to read from a “snapshot” of the database
Two Phase Locking Protocol
- A Protocol that insures conflict-serializable schedules
- Assures serializability
- Conflict serializable schdule에 대한 필요조건은 아니야
- Transaction이 final lock을 acquire 시점에 의해 serializability가 결정됨을 보여준다.
- Recoverability 보장 (Strict 2PL, Rigorous 2PL: OK Basic 2PL은 보장 x)
- Deadlock free를 보장하는 건 아니야
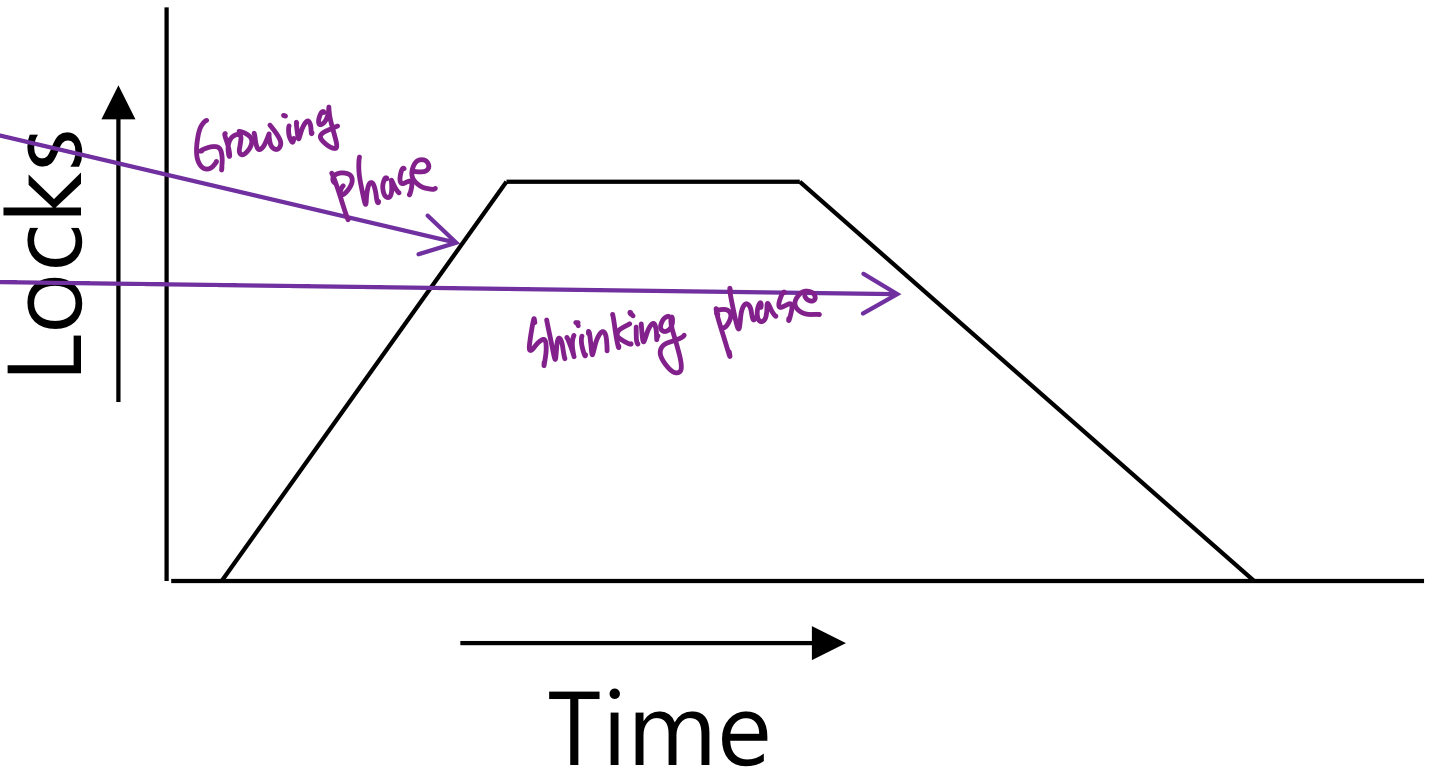
- Phase 1
- Transaction may obtain locks
- Transaction may not release locks
- can convert S-lock to X-lock
- Phase 2
- Transaction may release locks
- Transaction may not obtain locks
- can convert a X-lock to S-lock (당연, 나 제외 이 lock을 쓰지 않아)
두가지 버젼 존재
- Strict two-phase locking: Exclusive lock들에 대해서만 hold한다.
- Rigorous two-phase locking: 모든 lock에 대해 hold 해
- Transaction can be serialiezed in the order in which they commit
- Ensures recoverability and **avoids cascading roll-backs.
Graph Based Protocol
Graph based protocols alternative to two phase locking
- Transaction에서 data를 접근하는 순서를 정한다.
- D = {di, d2, …, dh}
- D는 directed acyclic graph가 될거야 (a.k.a. database graph)
Tree Based Protocols
Tree protocol is simple kind of graph protocol
- Only exclusive locks are allowed.
- E의 lock을 잡기위해서는 A, B, E lock을 잡고 있어야해
- 같은 transaction이 특정 data의 lock을 풀고 바로 다시 같은 lock을 잡는건 불가능 해
- Data item may be unlocked at any time
- Schedules not possible under two phase locking are possible under the tree protocol, and vice versa (진짜 Vice versa도 성립!!)
장점
- Ensures conflict serializability
- Ensures no deadlock (roll back free)
- Shorter waiting time, increase in concurrency (b/c 언제든지 lock을 풀수 있으니까)
단점
- Protocol does not guarantee recoverability (b/c commit dependency 고려 x)
- No guarantee cascade freedom (b/c commit dependency 고려 x)
- Transaction이 사용하지 않는 data까지 lock을 걸어 (b/c parent에 대해 lock이 있어야만 자식도 lock을 걸을수 있으니까)
- Increase locking overhead, waiting time
- Potential decrease in concurrency