Buffer & Indexing
Storage Access
맨날 Disk에 접근하기에는 오래 걸리니 main memory( = buffer)에 copy of disk block store 하자
Buffer Manager
Subsystem responsible for allocating buffer space in main memory
작동방식은 OS가 Buffer을 Manage하는 방법과 같다.
백문불여일견
- Write에서는 Read와 달리 return 값이 없다.
- 볼수 있듯이 Write가 Disk의 data modification을 보장하지 않는다.
Replacement Strategy
Two Purpose
- Prevent Eviction -> Pinned Block
- Prevent Concurrent Access -> Shared Lock & Exclusive Lock
Pined Block
Block that is not allowed for Eviction. Each block has its own pin count
- Pin: Done before reading / writing data from a block, cnt++
- Unpin: Done when read / write is complete, cnt–
- pin count == 0 일 때만 Eviction 가능
Shared Lock & Exclusive Lock
- Shared Lock: Reader들이 사용하는 lock, 2 이상 값도 가질수 있다. (Read는 여러명 씩 가능)
- Exclusive Lock: Wirter이 쓰는 lock, 최대가 1이다. (Write는 무조건 1명씩 진행되어야 한다.)
- Shared lock annot be concurrently with exclusive lock
Buffer Replacement Policies
Buffer manager can use statistics: probability that a request will reference a particular table
File system may reorder writes leading corruption of data structures on disk
CAREFUL Ordering of writes can avoid many such problems
LRU is BAD in Database
1:N 관계에서 Join을 실행한다 가정하자
N쪽의 tuple들마늘 따로 생각해보면 다음과 같이 실행됨을 알수 있다.
Buffer Manager에서 연속적으로 MISS -> SUCKS
Queries access disks in well-defined patterns (e.g. sequential scans)
Toss Immediate
Evicts a block as soon as that block is processed
- buffer를 단순 scratch pad 쓰듯이 쓴다.
- Sequential scan에 좋다.
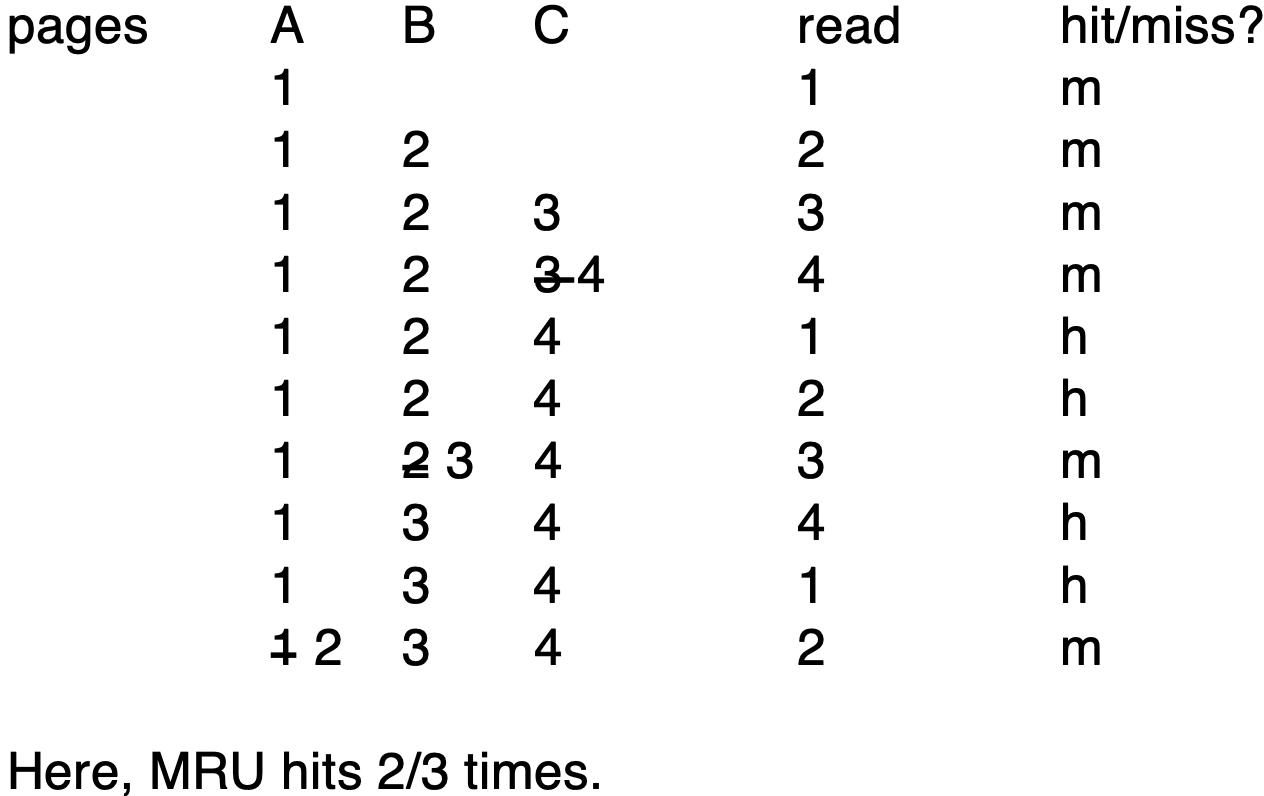
MRU (Most recently used)
제곧내
예시 출저
Indexing
Data를 더 빨리 찾으려고 만든 별도의 파일(Index file)
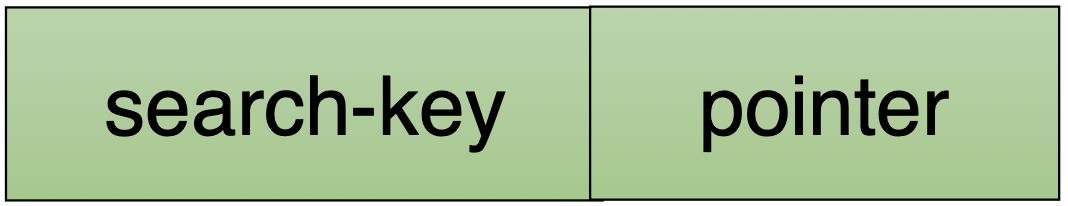
Index file consisst of records(called index entries) (below)
- Search Key: A set of attributes used to look up records
- Pointer: A reference to that row’s physical location (page + slot)
여기서 말하는 Indexing과 Slotted Page Structure 비교
- Slotted Page
- Layer: Within a single disk page (e.g. an 8 KB block)
- Role: define how variable-length records (or index entries) are laid out on that page
- Usage: every table file and every index file typically uses slotted pages under the hood
- B+ Tree(Indexing)
- Layer: Across many pages, as a file-level structure
- Role: implement an ordered index strategy: they organize (search-key → pointer) pairs into a height-balanced tree so you can do logarithmic‐time lookups, range scans, etc.
- Usage: each node of the B⁺-tree is itself stored in a slotted page, but the magic of the index is in how those pages link together (via parent/child pointers) to support fast searches.
- Two basic kinds of indices
- Ordered Indices: Keys are stored in sorted order(보통 tree 구조)
- Hash: Indices: Search keys are distributed uniformly across buckets using a hash function
- Index Evaluation Metrics
- Access types supported efficiently
- Point query: Hash works better
- Range query: Ordered Indices work better
- Access, Insertion, Deletion time
- Space overhead (Index structure가 차지하는 공간)
- Access types supported efficiently
Ordered Indices
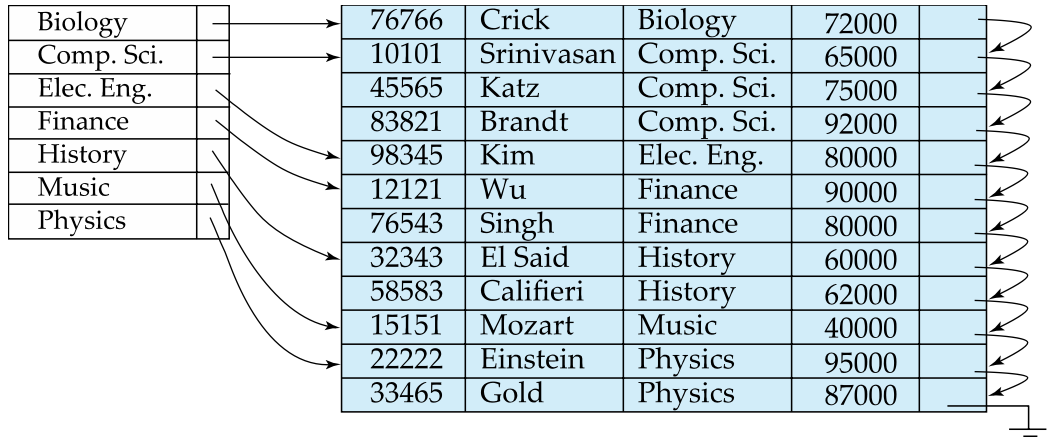
- Clustered index(primary index)
- Order of key in index == sequential order of file
- 즉, index의 순서대로 파일이 disk에 위치해 있다.
- 새로운 값이 들어와도 dynamic하게 order를 유지 시킴
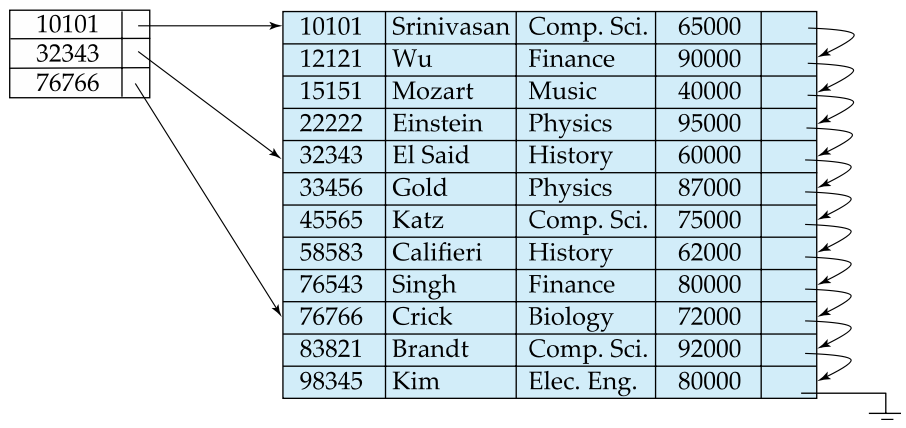
- Secondary index(nonclustered index)
- file 순서랑 index의 순서랑 따로 논다.
- Indexed-sequential file(ISAM)
Dense Index files
Index record appears for every search-key value in the file.
- Index file의 search-key들로 table 전체를 커버 할수 있으면 된다.
Sparse Index files
- Index file의 search-key들로 table 전체를 커버 불가.
- Applicable when records are sequentially ordered on search-key
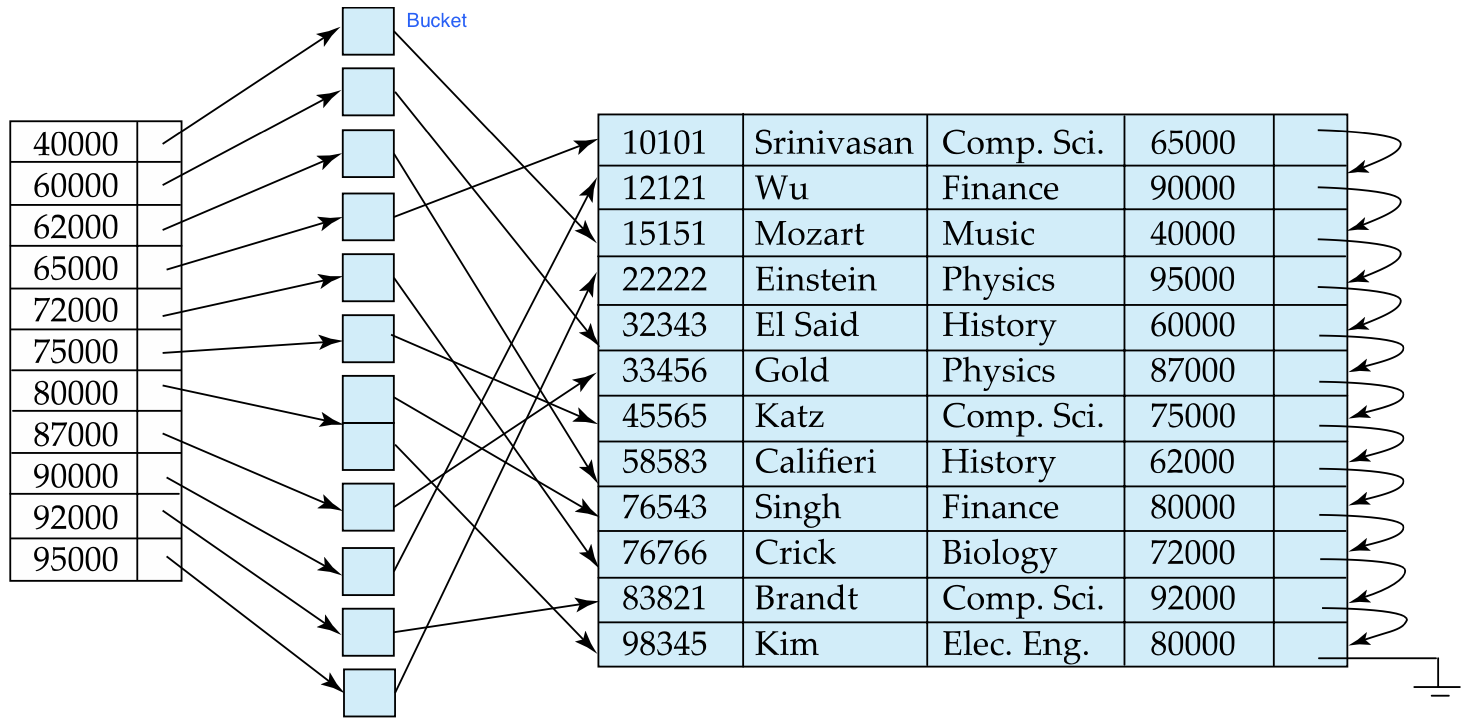
Secondary Indices
- index로 간략히 찾고, 실제 값은 bucket에서 찾아
- Hash table의 bucket 개념이랑 비슷
- Secondary indices have to be dense (b/c 아니라면 bucket에서 pointing할께 없잖아)
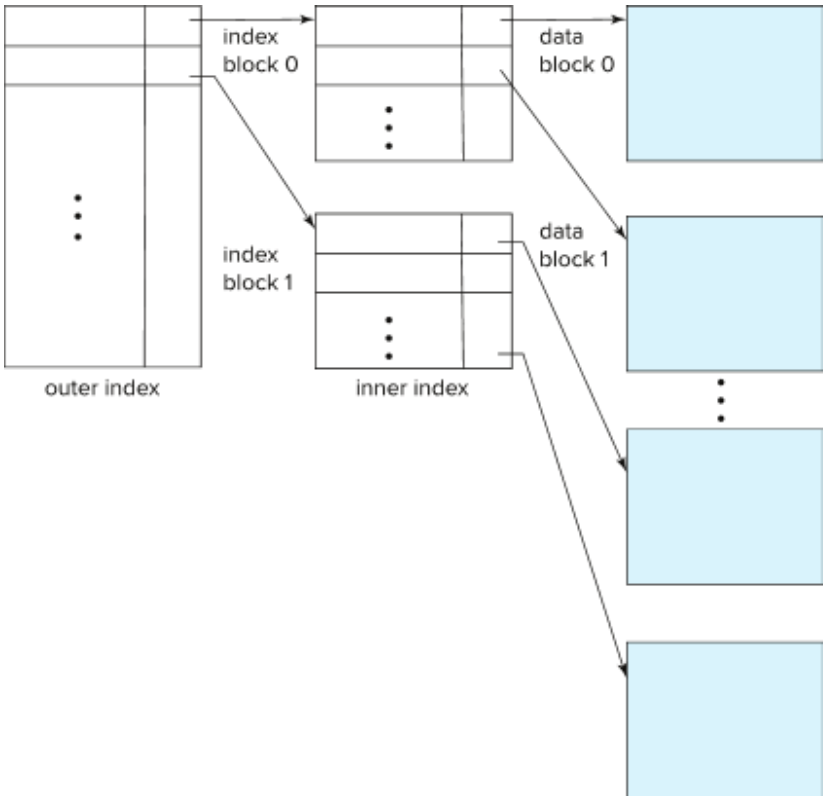
Multilevel Index
- Index가 memory에 다 들어가지 않을 경우
- => index file을 위한 index file을 위한 index file을 위한 index file을 위한 …
- Indices at all level must be updated on insertion or deletion from the file