01. Introduction to Database
01. Introduction to Database
Why use Database System
What is DBMS?
- Database(collection of data) Management system
- A collection of interrelated data and a set of programs to access those data
Drawback of file systems
- Data redundancy:
- e.g. Student A address data is used in data B and C
- Data Inconsistency: e.g. If student A’s data has been modified, All data that contains student A, also have to be changed
- Difficulty in accessing data:
- e.g. In DBMS we use unified query called sql, whereas needing separate program for file system
- Data isolation:
- e.g. .txt file and .png file is scattered in file system, caused by different file format
- Integrity problems:
- e.g. Students age should not be below zero
- Atomicity problems:
- e.g. think about @Transactional annotation in SpringDataJPA
- Concurrent-access anomalies
- e.g. a data is accessed concurrently
- Security problems
Data Models
Definitions – Collection of conceptual tools for Data, Data relationships, Data semantics, Consistency constraints
- Provides a way to describe the design og a database at yhe physical, logical, and view levels.
e.g.
- Relation Model
- Entity-Relationship Model
- Object Based Data Model
- Semistructed Data Model (e.g. XML)
Why use models?
Useful when examining or managing parts of the real world
e.g.
- Airplane simulator
- Nuclear power plant simulator
As can see on examples using a model is often much cheaper and safer
Types of data models
- Relation Model (Entity-Relationship data model)
- Object-based data models
- Semi-structured data model(XML)
View of Data
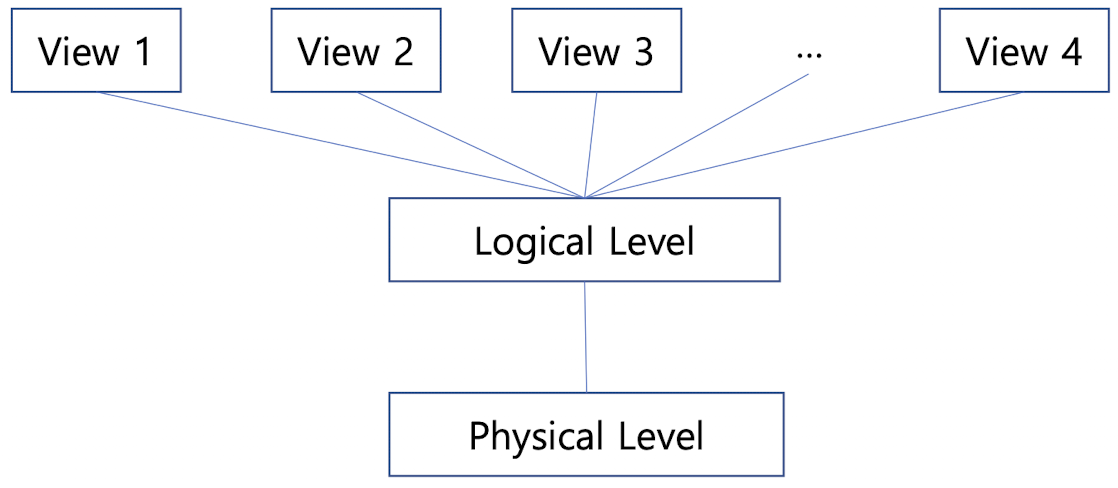 A major purpose of a database system is to provide users with an abstract view of the data. Database system hides certain details of how the data is stored and maintained
A major purpose of a database system is to provide users with an abstract view of the data. Database system hides certain details of how the data is stored and maintained
Data Abstraction
- Database systems must retrieve data efficiently, making database system developers to use complex data structures.
- Since many users are not computer trained it’s important to show abstract view
Physical level(Lowest level of abstraction)
- How data is actually stored, describes complex low-level data structure in detail
- e.g. Index structures (B+-tree, Hash table,…), Slotted page
Logical Level
1
2
3
4
5
6
Type instructor = record
ID: char(5);
name: char(20);
dept_name: char(20);
salary: numeric(8, 2);
end;
- What data are stored in the database, and what relationships exist among those data.
- e.g. Database administrators, who must decide what information to keep in the database, use the logical level of abstraction.
- usually programmers work at this level of abstraction.
Physical Data Independence
- The user of the logical level does not need to be aware of Insane complexity of physical level structures
- Ability to modify the physical schema without changing the logical schema
- In general, the interfaces between the various levels and components should be well-defined so that changes in some parts do not seriously influence others.
View Level(Highest abstraction level, a.k.a subschemas)
- Describes only part of the entire database.
- Exists to simplify their interation with the system.
- The system may provide many views for the same database.
- Hide details of logical level and provide a security mechanism
- e.g. student support team cannot see the instructor’s salary.
Schemas and Instances
Schema
- The overall design of the database
- Analogous to the type of variable
- Logical Schema: the overall logical structure(design) of the database
- Programmers construct applications by using the logical schema
- The physical schema is hidden beneath the logical schema, and can usually be changed easily without affecting application programs(physical data independence)
- Physical Schema: the overall physical structure(design) of the database
Instance
- the actual content of the database at a particular time
- Analogous to the value of a variable
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.